Sleeve Gastrectomy
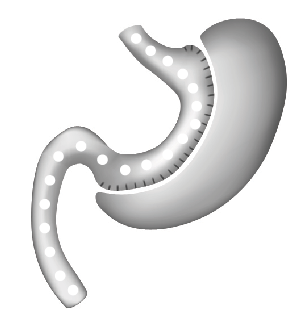
During a sleeve gastrectomy (SG) a narrow gastric tube is fashioned in-between the food pipe (oesophagus) and the small bowel, while the majority of the stomach (80%) is removed. The continuity of the stomach is not interrupted compared to a bypass procedure. The SG is a solely restrictive operation but since the removed part of the stomach is the major production area of the hunger hormone (Ghrelin), the Ghrelin level drops significantly after the SG, which decreases the food craving.
Hospital stay: usually 2-5 days
Weight loss: about 60 % of excess weight in 5 years. (Please be aware that the extent of weight loss is very individual and cannot be guaranteed.)
Following SG there is a rapid weight loss, but somewhat slower than after any gastric bypass surgery. The SG is considered to have slightly less complications compared to a bypass procedure. In few patients the long term weight loss after a SG might not be sufficient. In which case the sleeve can be converted to a bypass or loop – Duodenal Switch and adding a malabsorbtive component to the initially just restrictive procedure. This helps to achieve good additional weight loss.
A SG seems to be less efficient in binge eating (uncontrolled over eating) or sweet eating (preferably high-calorie sweets or beverages such as fruit juices, soft drinks) compared to a gastric bypass. After a SG preexisting heartburn can increase, which can require a live long anti acid medication. If despite medication the patients still experiences significant heartburn symptoms the SG might be converted to a bypass to separate the acid gastric content from the gastro-oesophageal junction, so reflux into the food pipe cannot occur.
The differences of a SG to the Roux-en-y gastric bypass, Omega loop bypass and Loop – Duodenal Switch are:
- According to current knowledge no regular three monthly vitamin B12 injections are required but periodic monitoring of the vitamin B12 level is strongly recommended.
- The residual stomach is still accessible by gastroscopy; therefore ERCP (endoscopy technique) can be used in case of gallstones blocking the bile duct.

